Diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels and other structures of the eyes, which can lead to the following eye diseases and conditions:
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Macular edema
- Cataracts
- Glaucoma
A comprehensive eye exam can detect early signs of diabetes. If you have diabetes or suspect you may have diabetes, visit us for a diabetic eye exam. We can monitor the health of your eyes and help prevent and manage sight-threatening eye diseases.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels resulting from the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar, allowing cells to absorb glucose for energy.
There are 3 main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes: Those with type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes can’t produce insulin because their body mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Individuals with type 1 diabetes rely on insulin injections.
- Type 2 diabetes: For those with type 2 diabetes, their body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use the insulin it makes. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type. Individuals can manage type 2 diabetes with lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity, medication, or insulin.
- Gestational diabetes: This type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy and is usually temporary. Gestational diabetes can increase a mother’s and the child’s risk of developing diabetes later in life.
How Can Diabetes Affect Your Eyes?
The link between diabetes and the eyes is multifaceted and can lead to various eye conditions, collectively known as diabetic eye disease. These conditions can include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, cataracts, and glaucoma.
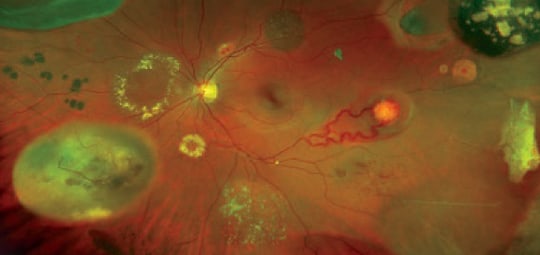
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a common complication of diabetes. It’s a sight-threatening condition and a leading vision loss concern for adults with diabetes. It occurs when elevated blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye.
In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy may not cause noticeable symptoms, but as it progresses, it can lead to the following symptoms:
- Blurry vision
- Black spots or holes in your field of vision
- Flashes of light in your field of vision
- Floaters in your field of vision
- Loss of vision
Diabetic Macular Edema
Macular edema is a complication of diabetes that can cause fluid to accumulate in the macula, the part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. The symptoms of diabetic macular edema can include:
- Blurry vision
- Straight lines appearing wavy
- Dark spots in your vision
Cataracts
Diabetes increases your risk of developing cataracts, a clouding of the eye’s lens that impairs vision. While cataracts are a common age-related condition, people with diabetes may develop them at an earlier age.
Symptoms of cataracts can include:
- Blurry vision
- Halos around lights
- Increased glare
- Reduced colour vision
Glaucoma
Diabetes can also raise your risk of developing glaucoma, a group of eye conditions often related to eye pressure that can damage the optic nerve, leading to vision loss. Diabetes can cause abnormal blood vessel growth that blocks fluid drainage systems in the eyes and contributes to increased eye pressure and an increased risk of glaucoma.
The Importance of Diabetic Eye Exams
Routine diabetic eye exams can help preserve your vision by detecting eye complications early—when they are often most treatable. These comprehensive eye exams go beyond the standard vision check and involve a thorough evaluation of the retina and other structures at the back of the eye.
If you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, you should have a diabetic eye exam every year. A diabetic eye exam may include the following procedures:
- Dilating your pupils: Dilating the pupils (the center part of the eye) helps us get a clear view of your retina. While the dilation may temporarily blur your vision, it is a crucial step in identifying early signs of diabetic eye disease.
- Assessing your retina: We will carefully examine your retina for any signs of diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, or other abnormalities. Early detection enables timely intervention to help prevent or slow the progression of these conditions.
- Measuring intraocular (eye) pressure: Checking intraocular pressure is essential for detecting glaucoma. People with diabetes should be vigilant about getting their eye pressure tested and speaking with their eye doctor about their risk of developing glaucoma.
- Tests for cataracts: While cataracts can be a natural part of aging, people with diabetes should be especially proactive in getting cataract testing.
Reduce Your Risk with Regular Eye Exams in Calgary
Many Canadians live with diabetes. With comprehensive eye exams and diabetic eye exams, we can help detect the signs of diabetes and diabetic eye diseases early. An early diagnosis and routine care can help you maintain your long-term eye health and sight.If you have diabetes or want to rule out the condition, book an eye exam with Eyesis Eyecare.